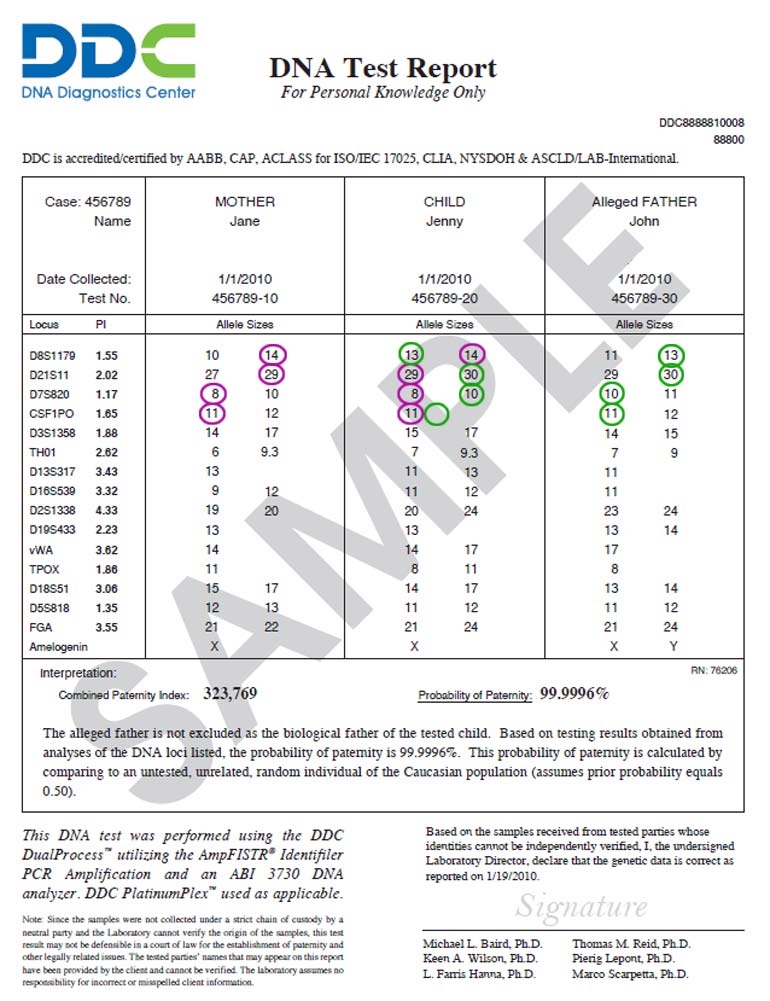
To determine if a DNA test might be fake or unreliable, consider the following signs:
Lack of Accreditation: Legitimate DNA testing labs are accredited by recognized bodies like the AABB (American Association of Blood Banks) or ISO. If a lab lacks accreditation, it’s a red flag.
Unprofessional Results: Real DNA test results include detailed information, such as chain-of-custody documentation (for legal tests), and often include statistical probabilities. Results that are vague or overly simplistic may be suspect.
No Chain of Custody: For legal DNA tests, a strict chain of custody process is required to ensure the integrity of the samples. If a test claiming to be for legal purposes skips this step, it’s likely not legitimate.
Inconsistent Communication: If the company providing the test is hard to reach, provides unclear or contradictory information, or lacks transparency in their processes, it’s a cause for concern.
Too-Good-to-Be-True Offers: Be wary of companies offering DNA tests at prices significantly lower than reputable services, especially without clear information about lab processes and accreditation.
Unverified Collection Methods: Legitimate DNA tests often require specific sample collection methods, such as cheek swabs or blood samples, collected in a controlled environment. If the collection method seems unscientific or unreliable, the test may be fake.

